Understanding The Visual Turing Test: An In-Depth Exploration
The Visual Turing Test is an essential concept in the intersection of artificial intelligence and human perception. In today's digital landscape, where visuals play a pivotal role in communication and interaction, understanding this test is more relevant than ever. As technology advances, the ability for machines to interpret and replicate human-like visual understanding becomes a crucial measure of their intelligence. This article delves into the nuances of the Visual Turing Test, its significance, and the implications it holds for the future of AI.
In this article, we will explore the foundational concepts of the Visual Turing Test, its historical context, and its application in various fields. We will also look at how it compares with traditional Turing tests and the challenges faced in evaluating visual intelligence in machines. By the end of this exploration, readers should have a comprehensive understanding of the Visual Turing Test and its impact on the development of artificial intelligence.
Join us as we embark on this journey to uncover the complexities of visual intelligence and its significance within the realm of AI. Through thorough analysis and expert insights, we aim to provide valuable information that enhances your understanding of this fascinating topic.
Table of Contents
- What is the Visual Turing Test?
- Historical Context of the Visual Turing Test
- Importance of the Visual Turing Test
- Visual Turing Test vs. Traditional Turing Test
- Applications in AI
- Challenges and Limitations of the Visual Turing Test
- The Future of the Visual Turing Test
- Conclusion
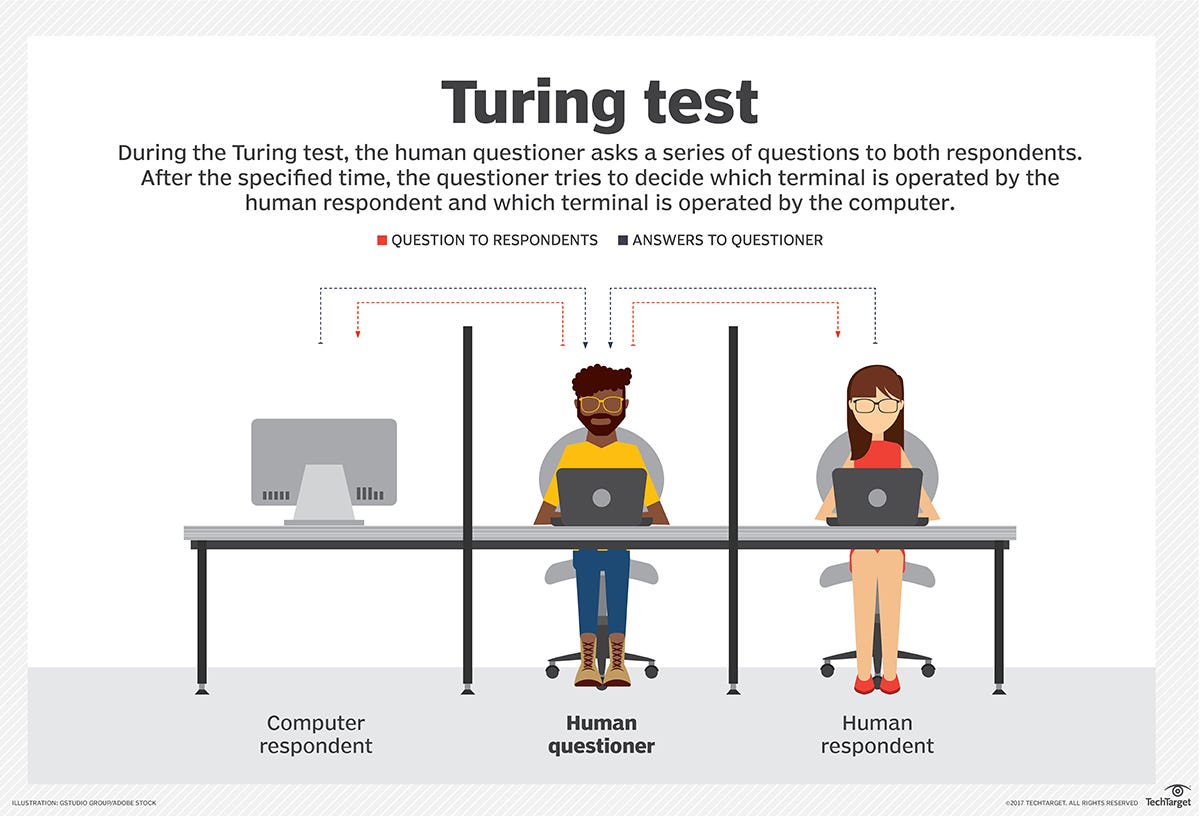
What is the Visual Turing Test?
The Visual Turing Test is a framework designed to assess a machine's ability to interpret and generate visual content in a manner indistinguishable from human capabilities. Unlike the traditional Turing Test, which evaluates conversational ability through text-based interaction, the Visual Turing Test focuses specifically on visual understanding and perception.
This test involves presenting a series of visual stimuli, such as images or videos, to both human evaluators and AI systems. The goal is to determine whether the AI can produce visual outputs that are perceived as human-like, effectively creating a challenge for machines to demonstrate their understanding of complex visual cues, context, and subtleties.
Historical Context of the Visual Turing Test
The concept of the Visual Turing Test emerged from the foundational ideas established by Alan Turing in 1950. Turing's original test aimed to evaluate a machine's ability to exhibit intelligent behavior equivalent to, or indistinguishable from, that of a human. Over the years, as technology evolved, so did the understanding of intelligence, leading to the development of tests that specifically assess various forms of intelligence, including visual intelligence.
The Visual Turing Test gained traction in the early 21st century, coinciding with advancements in computer vision and artificial intelligence. Researchers began to recognize the importance of visual perception in AI, leading to a growing body of literature and experimentation surrounding this area. The test serves as a benchmark for evaluating how far AI has come in mimicking human visual understanding.
Importance of the Visual Turing Test
The importance of the Visual Turing Test lies in its ability to bridge the gap between human perception and machine intelligence. As AI systems are increasingly integrated into everyday applications, the need for machines to understand and interpret visual data becomes paramount. Here are some key reasons why the Visual Turing Test is crucial:
- Enhancing AI Capabilities: By assessing visual intelligence, researchers can improve AI systems' ability to analyze and interpret visual information accurately.
- Quality Control: The test can be used to validate the effectiveness of AI-driven visual recognition systems, ensuring they meet human-like standards.
- User Experience: Improving the visual perception of AI can enhance user interactions and experiences in applications ranging from virtual assistants to self-driving cars.
- Ethical Implications: As AI continues to evolve, understanding its limitations and capabilities in visual recognition is essential for ethical development and deployment.
Visual Turing Test vs. Traditional Turing Test
While both the Visual Turing Test and the traditional Turing Test measure intelligence, they differ fundamentally in their approach. The traditional Turing Test evaluates conversational intelligence through text-based dialogue, focusing on linguistic capabilities and cognitive responses. In contrast, the Visual Turing Test specifically addresses the visual domain, examining how well AI systems can interpret and generate visual content.
Key Differences:
- Medium: Traditional Turing Test uses text; Visual Turing Test uses visual stimuli.
- Focus: Traditional focuses on language and communication; Visual focuses on visual understanding and perception.
- Evaluation Criteria: Traditional evaluates logical reasoning and conversational flow; Visual evaluates visual interpretation and contextual understanding.
Applications in AI
The Visual Turing Test has various applications across different fields of artificial intelligence, influencing how machines interact with and understand the visual world. Here are some notable applications:
1. Computer Vision:
Computer vision systems utilize the Visual Turing Test to enhance their ability to recognize objects, scenes, and actions within images and videos. By passing this test, AI can achieve higher accuracy in tasks such as image classification, object detection, and scene understanding.
2. Autonomous Vehicles:
In the realm of autonomous driving, the Visual Turing Test is vital for ensuring that vehicles can interpret their surroundings accurately. This includes recognizing traffic signs, pedestrians, and obstacles, enabling safe navigation in complex environments.
3. Robotics:
Robotic systems benefit from the Visual Turing Test by improving their ability to perceive and interact with the physical world. This is crucial for applications in manufacturing, healthcare, and service industries, where robots need to understand visual cues to perform tasks effectively.
4. Creative Applications:
AI-generated art and design are also evaluated through the Visual Turing Test. By assessing whether AI can produce visually appealing and contextually relevant content, researchers can push the boundaries of creativity in technology.
Challenges and Limitations of the Visual Turing Test
Despite its significance, the Visual Turing Test faces several challenges and limitations that researchers must address:
- Subjectivity: Human perception is inherently subjective, making it difficult to establish standardized criteria for evaluation.
- Complexity of Visual Data: The vast diversity of visual stimuli poses challenges in creating comprehensive test scenarios that accurately represent real-world conditions.
- Technological Limitations: Current AI systems may still struggle with certain visual tasks, highlighting the need for continued research and development.
- Ethical Concerns: As AI becomes more adept at mimicking human visual understanding, ethical implications regarding privacy and security arise.
The Future of the Visual Turing Test
The future of the Visual Turing Test is promising, with ongoing research aimed at refining its methodology and applications. As technology continues to advance, we can expect the following developments:
- Enhanced Evaluation Methods: New techniques for evaluating visual intelligence will emerge, incorporating machine learning and advanced statistical analysis.
- Integration with Multimodal AI: Future tests may incorporate multiple forms of intelligence, assessing how well AI can integrate visual perception with other cognitive abilities.
- Broader Applications: The relevance of the Visual Turing Test will expand across diverse industries, including healthcare, entertainment, and education.
- Ethical Frameworks: As AI visual capabilities grow, establishing ethical guidelines for their use will become increasingly important.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Visual Turing Test stands as a vital measure of artificial intelligence's ability to understand and generate visual content. As we move forward in a world increasingly influenced by AI, grasping the implications of this test becomes essential for developers, researchers, and the general public. By fostering a deeper understanding of visual intelligence, we can better navigate the complexities of technology and its impact on our lives.
We encourage readers to engage with this topic further. Share your thoughts in the comments, discuss with peers
Discovering Davos: A Comprehensive Guide To Where Is Davos
Error Code 232011: Understanding And Resolving The Issue
Exploring The Fascinating World Of 70s Sci-Fi Movies